What you need to know about Xanthelasma
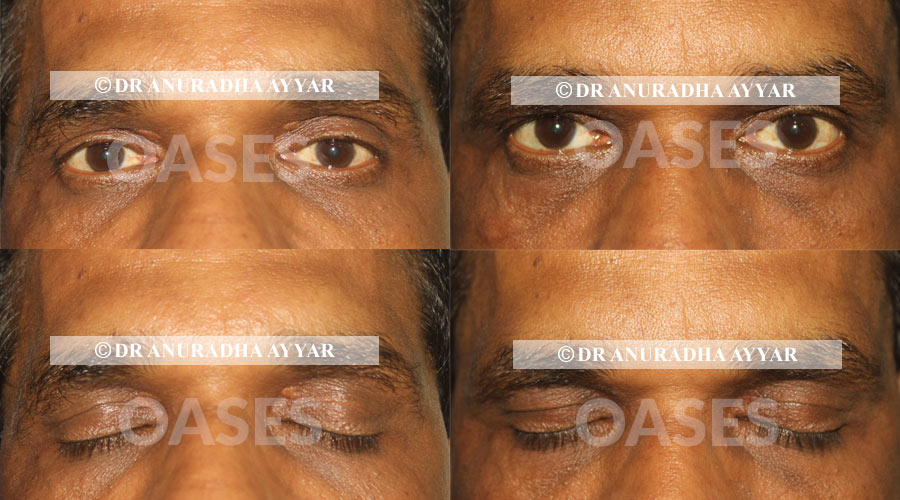
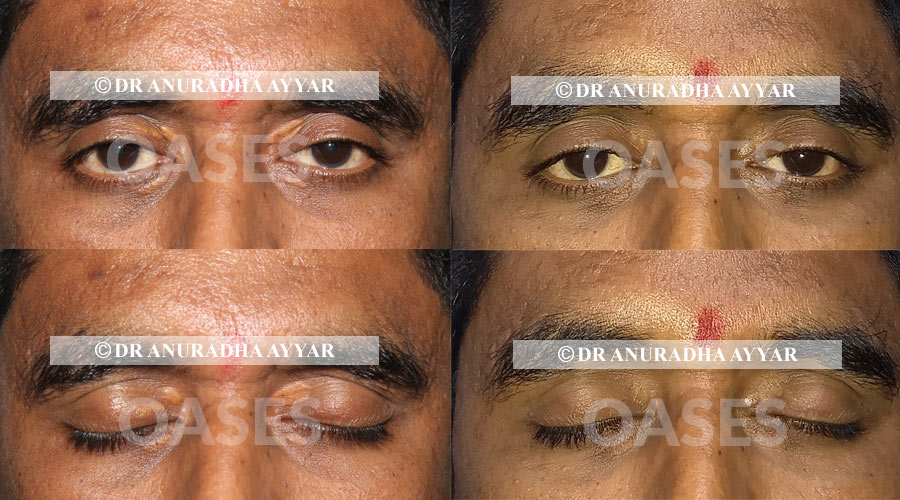
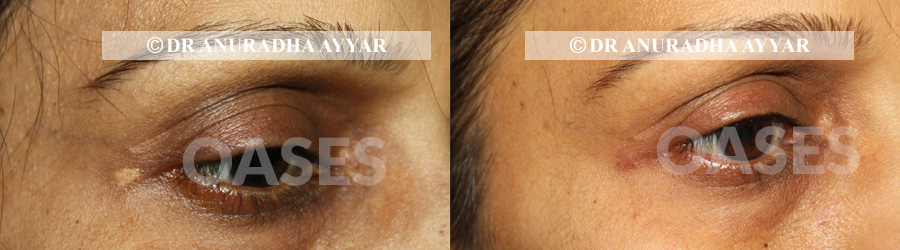
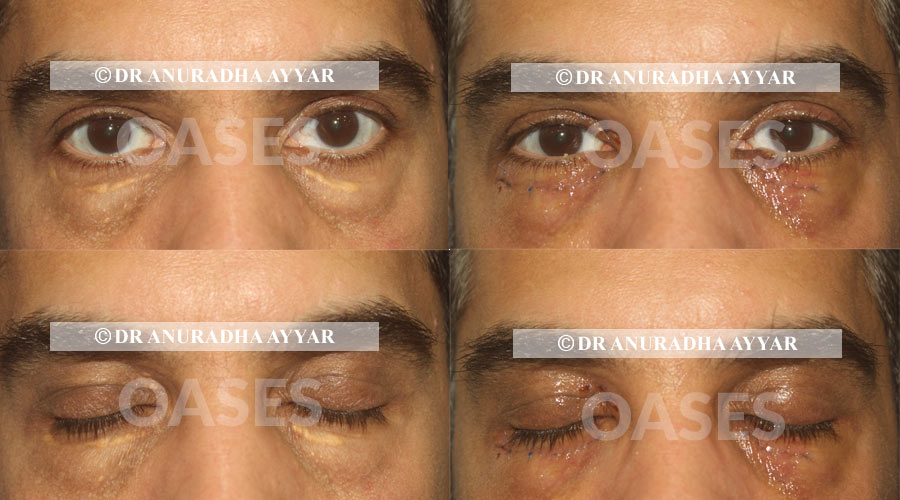
patients between ages of 38-60 years with cholesterol deposits in the eyelid skin (xanthelasma) have undergone excision of the damaged skin with cosmetic skin closure with fine sutures.
While there are options of lasers or chemical peels for this issue, both require multiple sittings with a high rate of scarring and incomplete removal. Surgical approach allows removal of the entire existing lesion and converts an unsightly condition into very fine linear scars that fade with time.
While most cases of xanthelasma are idiopathic, some are hereditary while others may be associated with thyroid abnormalities, lipid profile issues. The oculoplasty surgeon will assess each pateint in detail to determine cause and advice treatment.
Strict control of systemic diseases, healthy life style may prevent or delay recurrence.
-
Patient 1: 3 months follow up shows no scar
-
Patient 2: 1 year follow up shows no scar
-
Patient 3: 10 days follow up after suture removal. the redness subsides in few days and skin tone returns to normal
-
Patient 4: first post surgery day with sutures in place.
Xanthelasma - cholesterol deposit in the eyelids
High levels of cholesterol don't just endanger your heart by clogging up your arteries but can also result
as deposits in the eyelids. These deposits, often yellow in colour, form around the eyelids and may not
be accompanied with other symptoms initially. This condition is referred to as xanthelasma, may not hurt
your eyes, but can be a sign of an underlying medical condition. These deposits, that appear as patches,
on the eyelids, can be removed by an eye specialist, in particular, an Oculoplasty surgeon.
Symptoms of xanthelasma
The most common and obvious symptom of this condition is the formation of yellow patches on the
eyelids. These may occur in the upper or lower eyelids or on the outer aspect of the eyelid skin. Based
on the severity of the condition, the size of the deposits may change over time: it tends to increase with
time.
Causes and risk factors of xanthelasma
While there may be no specific cause found for this condition in some patients, here are certain factors
that can increase the risk of developing these patches. These include:
-
High cholesterol levels in the blood. However, in some cases these deposits may occur even
when cholesterol levels are normal.
-
Genetic history
-
Liver condition
-
Lipid disorder (dyslipidemia)
-
High levels of triglycerides or LDL
-
Thyroid gland abnormalities
-
Low levels of HDL
-
Lifestyle factors such as excessive consumption of alcohol, poor nutrition, high-fat diet, low
activity levels, obesity, smoking etc.
-
Use of certain medicines such as beta blockers, corticosteroids etc.
Diagnosing xanthelasma
In case you notice such deposits on your eyelids, be sure to schedule an appointment with an eye
specialist (Oculoplasty doctor). The doctor will do a physical exam and ask about your medical (and
family) history. You may also be asked to do a blood screening to check cholesterol, thyroid hormonal
profile and other lipid protein levels.
Treating xanthelasma
Treatment for these deposits is usually sought for cosmetic reasons and should ideally be done by an
Oculoplastic surgeon. Some of the treatment options include:
-
Surgical removal of deposits with a small, precise blade. This is a common treatment method
and often is done with minimal scarring. The main advantage is that this is a single sitting treatment
option.
-
There are other options like chemical peels, lasers etc. But these are not recommended due to
following reasons
-
1. Xanthelasma deposits occurs between the eyelid skin and muscle beneath.
-
2. The eyelid skin is the thinnest in the body. So lasers and peels here can produce significant
scars and pigmentation issues while not removing the lesion entirely despite multiple sittings.
-
3. Much of the xanthelasma lesion is below the skin and will need surgical excision alone for
complete removal.
In addition, as these deposits largely occur due to high levels of fat or lipids in the blood, you may be
advised certain lifestyle habits to prevent them from recurring. These may include:
-
Adopting a low fat diet that is rich in fiber (healthy plant-based diet)
-
Reducing or eliminating smoking and alcohol consumption so as to reduce inflammation in the
body
-
Adding moderate exercise to your daily routine
Thus, in most cases, the deposits are not a problem in themselves but most occur due to an underlying
health condition. An Oculoplastic surgeon will be able to remove these deposits while a healthier lifestyle
can help prevent them from forming again.